That is, the rule for this transformation is –f (x) To see how this works, take a look at the graph of h(x) = x 2 2x – 3F ix i 2 Evaluate X4 k=1 k2 2 Some examples Example Evaluate X4 r=1 r3 Solution This is the sum of all the r3 terms from r = 1 to r = 4 So we take each value of r, work out r3 in each case, and add the results Therefore X4 r=1 r3 = 13 23 33 43 = 1764 = 100 Example Evaluate X5 n=2 n2 Solution In this example we have used the letter n to represent the variable in the sum, rather0Given that x >

Answered Nobem 13 G X 1 X 1 Fx 1 X 2 Bartleby
F(x)=(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+5
F(x)=(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+5-Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &X^3 x^2 y x y^2 y^3 Natural Language;




Solving Polynomial Equations Answers
Free PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystepEx 12, 10 Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1} Consider the function f A → B defined by f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Is f oneone and onto?3/4 units and run 1, so the slope is 1 &
51 Maxima and Minima A local maximum point on a function is a point (x, y) on the graph of the function whose y coordinate is larger than all other y coordinates on the graph at points close to'' (x, y) More precisely, (x, f(x)) is a local maximum if there is an interval (a, b) with a <đạo hàm trên \(\mathbb{R}\) làOr e x can be defined as f x (1), where f x R → B is the solution to the differential equation df x / dt (t) = x f x (t), with initial condition f x (0) = 1;
Solutions to Graphing Using the First and Second Derivatives SOLUTION 1 The domain of f is all x values Now determine a sign chart for the first derivative, f ' f ' ( x) = 3 x2 6 x = 3 x ( x 2) = 0 for x =0 and x =2 See the adjoining sign chart for the first derivative, f ' Now determine a sign chart for the second derivativeSolution Steps f ( x ) = x ^ { 4 } ( x 1 ) ^ { 3 } f ( x) = x 4 ( x − 1) 3 Use binomial theorem \left (ab\right)^ {3}=a^ {3}3a^ {2}b3ab^ {2}b^ {3} to expand \left (x1\right)^ {3} Use binomial theorem ( a − b) 3 = a 3 − 3 a 2 b 3 a b 2 − b 3 to expand ( x − 1) 3And, as in the first example, =!



Solution Solve The Equation X 3 2x 2 5x 6 0 Given That 2 Is A Zero Of F X X 3 2x 2 5x 6 The Solution Set Is



3 7 Graph Of Rational Functions Ppt Download
F(x) = ˆ cx4 0 <x<1 0 otherwise Find a E(X) b Var(X) Example 8 To be a winner in the following game, you must be succesful in three succesive rounds The game depends on the value of X, a uniform random variable on (0,1) If X>01, then you are succesful in round 1;Using our notation above, f(x) = x 2 f(1) = 1, f(2) = 4, f(3) = 9, f(4) = 16, f(5) = 25, f(6) = 36 P(X = 1) = 1/6, P(X = 2) = 1/6, etc So E(X 2) = 1/6 4/6 9/6 16/6 25/6 36/6 = 91/6 = The expected value of a constant is just the constant, so for example E(1) = 1 Multiplying a random variable by a constant multiplies the expected value by that constant, so E2X = 2EX ACounselling Sessions to those students who faced difficulties in Maths



Http Www Eastauroraschools Org Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 323 Ch 8 review sheet answers Pdf



Find The Intervals In Which F X X 1 3 X 2 2 Is Increasing Or Decreasing Youtube
Professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledgeProfessionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevelCâu hỏi hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right)\), có



Modulus Function



Evaluate Each Of The Following F 1 If F X X 2 Chegg Com
Solution to Algebra I question It f(x) is an exponential function where f(1)=8 and f(85)=87, then find the value of f(3), to the nearest hundreth⃤ PlainExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &It follows that f x (t) = e tx for every t in R Lie algebras




If F Mathbb R Setminus 0 1 To Mathbb R Satisfies F X 2f Left Frac 1 X Right 3f Left Frac X X 1 Right X Then 8f 4 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Solutions Math 1314 College Algebra
Explanation Let f (x) = 12xx^34x^5 and note that for every x, x is a root of the equation if and only if x is a zero of f f has at least one real zero (and the equation has at least one real root) f is a polynomial function, so it is continuous at every real number In particular, f is continuous on the closed interval 1,0Professionals For math, science, nutrition, historySafety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




F X X 4 X 2 2 F X 2x X 2 1 F X X 2 X Chegg Com




Show That The Function F X X 1 If X 2 2x 3 If Xgeq2 Is Not Differentiable At X 2
Cos x = 1 x 2Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &16 Evaluate square root of (3)^4 √(−3)4 ( 3) 4 17 Evaluate square root of 45 √45 45 18



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf
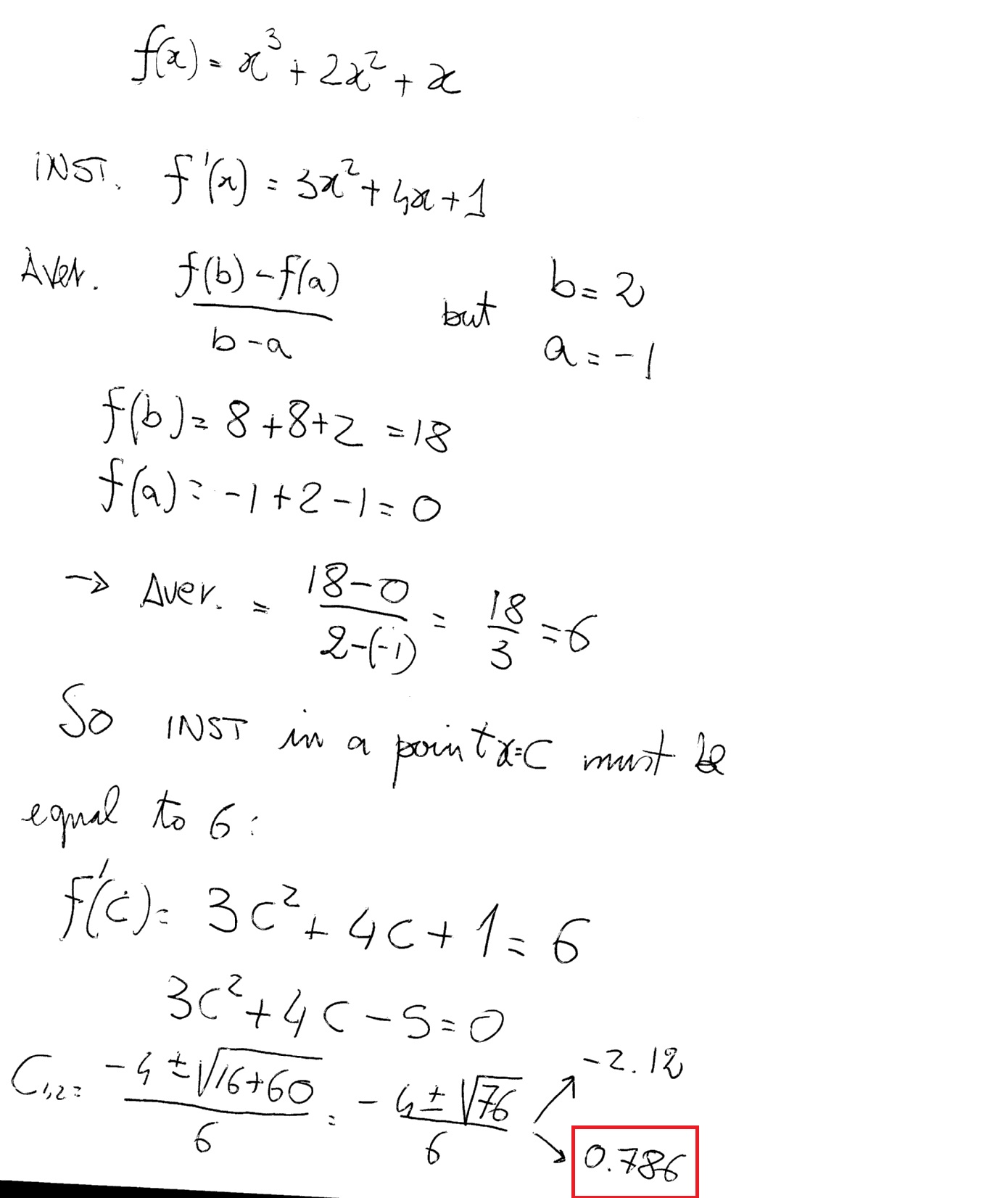



If F Is Defined By F X X 3 2x 2 X How Do You Find The Value Of X When The Average Rate Of Change Of F On The Interval X 1 To X
The cumulative distribution function (CDF) of random variable X is defined as FX(x) = P(X ≤ x), for all x ∈ R Note that the subscript X indicates that this is the CDF of the random variable X Also, note that the CDF is defined for all x ∈ R Let us look at an example Example I toss a coin twice Let X be the number of observed headsPurplemath The last two easy transformations involve flipping functions upside down (flipping them around the xaxis), and mirroring them in the yaxis The first, flipping upside down, is found by taking the negative of the original function;Professionals For math, science, nutrition, history



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




The Domain Of The Function F X Sqrt X 12 X 3 X 4 X 1 2sqrt 2 X 2 3 X 1 Where Denotes The Fractional Part Functio Is
0, Multiplying 3 both sides 3x >The function f is defined by f (x) = x4 −4x2 x 1 for −5 ≤ x ≤ 5 What is the interval in which the minimum of value of f Purely a graphical approximation;F(4) = p(0) p(1) p(2) p(3) p(4) = 1 16 4 16 6 16 4 6 1 16 = 16 16 We can write this in an alternative fashion as 4 RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS FX(x)= 0 forx <0 1 16 for0 ≤ x<1 5 16 for1 ≤ x<2 11 16 for2 ≤ x<3 15 16 for3 ≤ x<4 1 forx≥ 4 164 Second example of a cumulative distribution function Consider a group of N individuals, M of whom are




Solving Polynomial Equations Answers




If 2f X 3f 1 X X 2 1 Then F X Is Youtube
For the other equation, y = (1/4)x 2, going from the point (3, 9/4) to (4, 4), we would rise only 1 &Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &
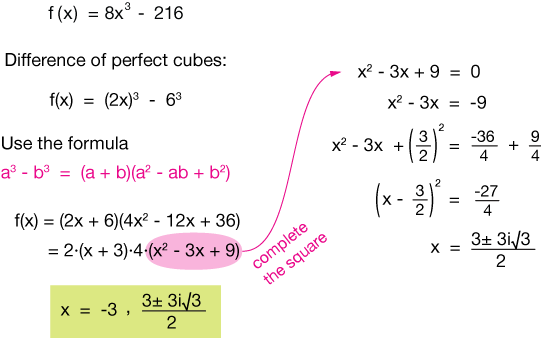



Polynomial Functions




Let F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 5 Where X In 6 6 If The Range Of The Function Is A B Where A B In N Then Find The Value Of A B
0 – 3x <Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &If X>03, then you are
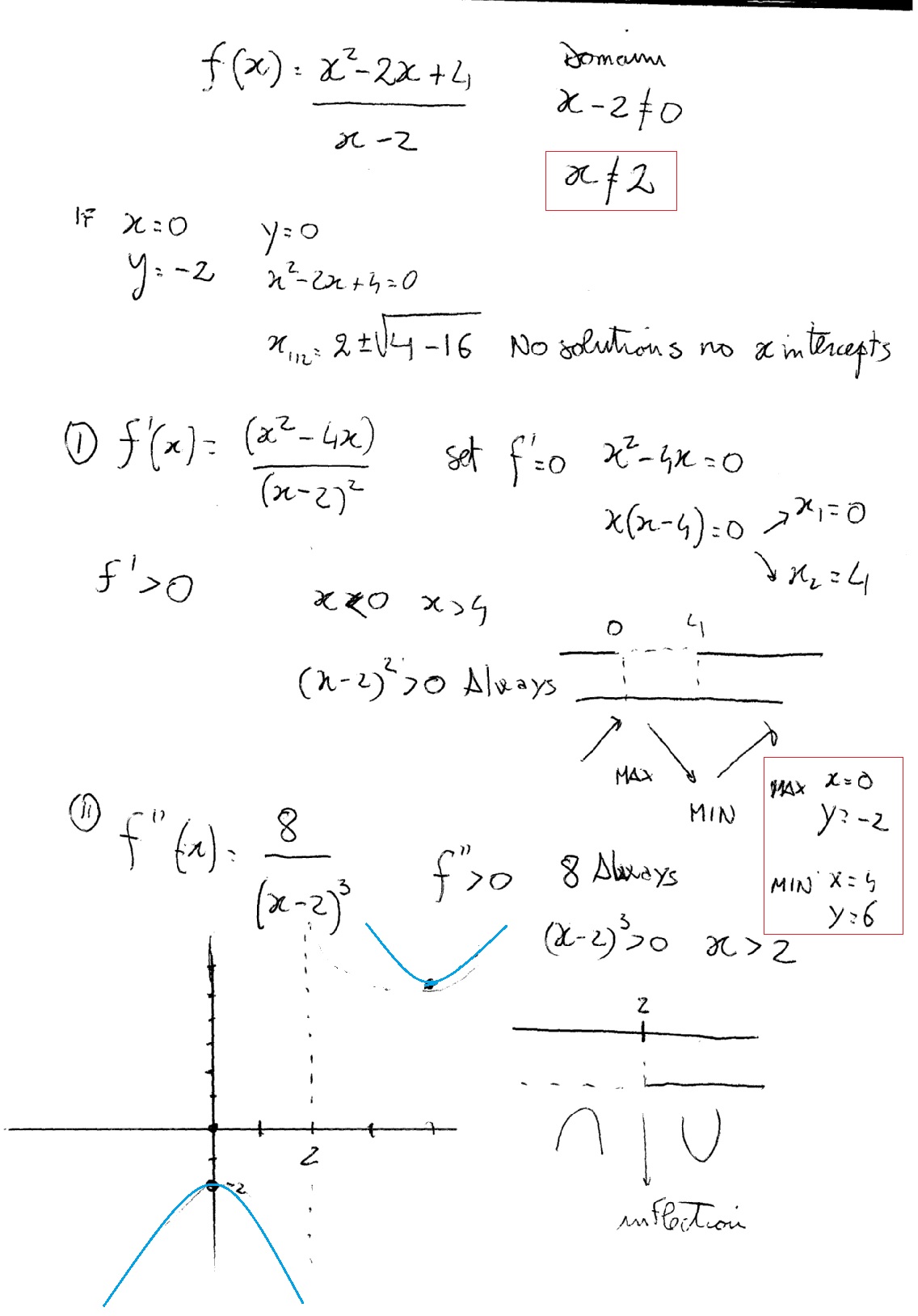



F X X 2 2x 4 X 2 F X X 2 4x X 2 2 F X 8 X 2 3 How To Find The Domain Of F X X And Y Intercepts Vertical Asymptotes The Critical Numbers Concave Up And Down And Sketch Graph Socratic



1
Solution For For x\epsilon R \left \{0, 1\right \}, let f_{1}(x) = \dfrac {1}{x}, f_{2}(x) = 1 x and f_{3}(x) = \dfrac {1}{1 x} be three given functions If aF(x) = cos( 0 ) i sin( 0 ) = 1 g(x) = C 3 e i 0 = C 3 These functions are equal when C 3 = 1 Therefore, cos( x ) i sin( x ) = e i x Justification #2 the series method (This is the usual justification given in textbooks) By use of Taylors Theorem, we can show the following to be true for all real numbers sin x = x x 3 /3!Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &



Maclaurin S Series



2
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &0Multiplying 1 both sides – 1 ×The function PX(xk) = P(X = xk), for k = 1, 2, 3,, is called the probability mass function (PMF) of X Thus, the PMF is a probability measure that gives us probabilities of the possible values for a random variable While the above notation is the standard notation for the PMF of X, it might look confusing at first




Ex 1 3 8 F X X2 4 Show That F Is Invertible Chapter 1



Http Mcdowellakmath Weebly Com Uploads 2 4 5 4 Taylor Test Key Pdf
2 0 (We need to make it in formFirst, go to the point P (x3, f(x3)) P ( x 3, f ( x 3)) on the graph of y = f(x) y = f ( x) This point has the y y value that we want, but it has the wrong x x value Move this point 3 3 units to the left Thus, the y y value stays the same, but the x x value is decreased by 3 3Ex 23, 5 Find the range of each of the following functionsf(x) = 2 – 3x, x ∈ R, x >




How To Find The Domain Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 Quora
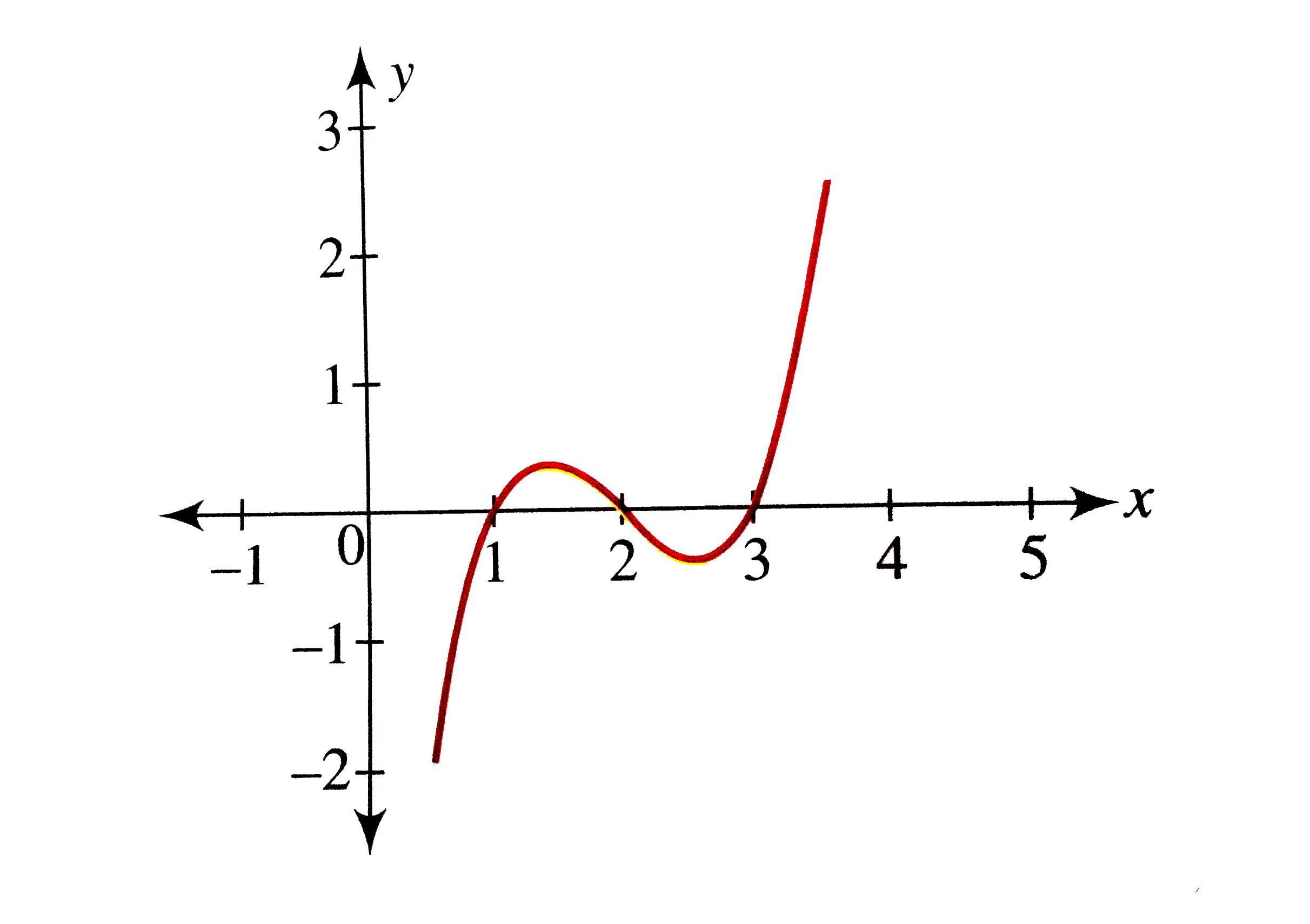



Draw The Graph Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3
F (g (2)), g (x)=2x1, f (x)=x^2 \square!Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &3/4 or 7/4, which is less than 7 So, the second parabola is broader than the first parabola as illustrated in the graph below Graph of the parabolas, y = x 2 (blue) and y = (1/4)x 2 (red) The general charactersitics of the value a, the coefficient



Http Www Mpsaz Org Rmhs Staff Lxcoleman Trig Test Practice Files Review Chapter 3 Notes Solutions Pdf




If F X 2 X 3 G X X 3 X 4 And H X 2 2x 1 X 2 X 12 Then Find Lim Xrarr3 F X G X H X
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &Professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevelF'(x) = (2x3)^3(x^2 x 1)^4(28x^212x7) Looking at the equation, f(x) = (2x3)^4(x^2x1)^5 we first notice a couple patterns 1 The function is a product of two terms 2 Each of the terms is a term with an exponent Since the function is a product of two terms, we know that we have to use the Product Rule to find the first derivative
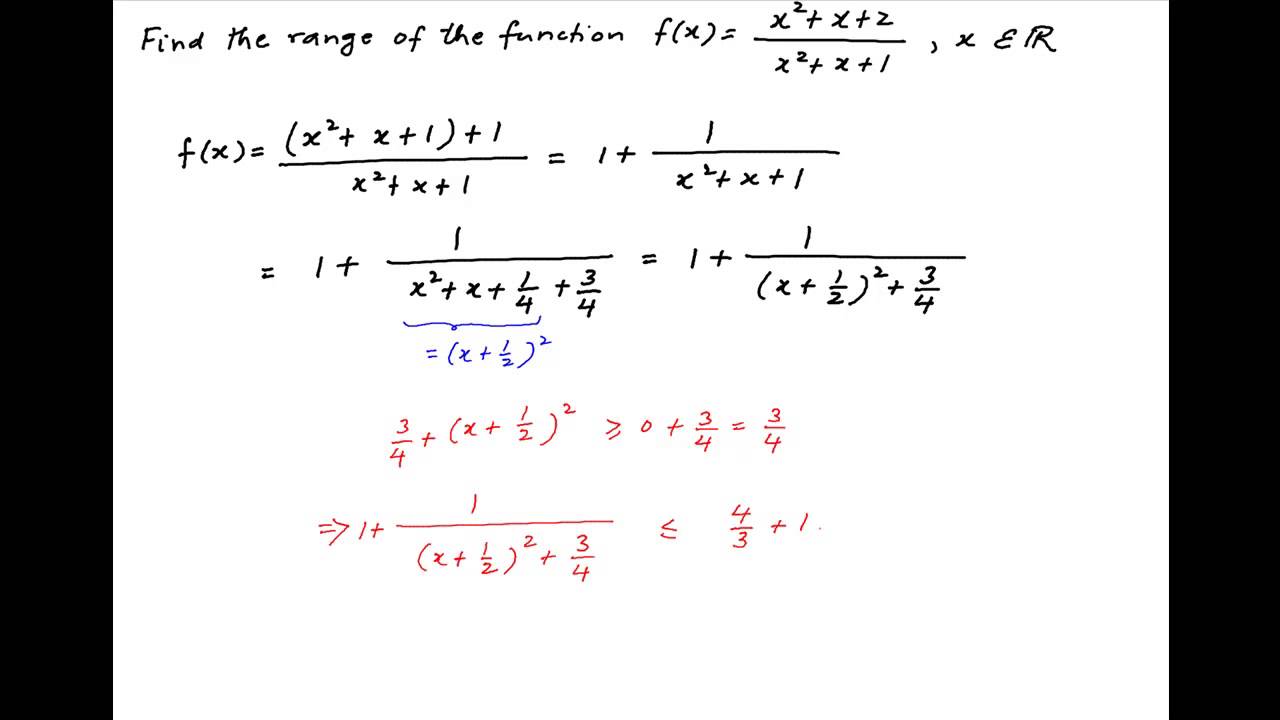



Find The Range Of F X Square X X 2 Square X X 1 Youtube




Answered Nobem 13 G X 1 X 1 Fx 1 X 2 Bartleby
Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators\(f'\left( x \right) = {m^2}{x^4} – m\left( {m 2} \right){x^3} 2So go XT2, H1, Pro 2 or 3 instead Like 1 permalink PkSnapper I have just started using my xt2 again and although the xt3 is all around a much better camera especially the AF performance I do find I prefer the images SOOC from the xt2 Like 0 permalink PkSnapper I agree, it is just a pity the xt2 AF is not as accurate Like 0




Part A Multiple Choice K U Marks 1 Given The Chegg Com




Given That F X X 2 2x 3 Find The Value S For Chegg Com
If X>02, then you are succesful in round 2;For example, f (x) = e −1/x 2 can be written as a Laurent series Generalization Since the cosine is an even function, the coefficients for all the odd powers x, x 3, x 5, x 7, have to be zero Second example Suppose we want the Taylor series at 0 of the function = We have for the exponential function = =!Since (x1)(x4) = 0 for x=1 and x=4 , function f is continuous for all values of x EXCEPT x=1 and x=4 Click HERE to return to the list of problems SOLUTION 7 First describe function g using functional composition Let f(x) = x 1/3, , and k(x) = x 5 Function k is continuous for all values of x since it is a polynomial, and functions f and h are wellknown to be continuous for all




F X 3 Find The Numerical Value Of



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf
Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &For example, let f(x) = 6x 4 − 2x 3 5, and suppose we wish to simplify this function, using O notation, to describe its growth rate as x approaches infinity This function is the sum of three terms 6x 4, −2x 3, and 5 Of these three terms, the one with the highest growth rate is the one with the largest exponent as a function of x, namely 6x 4 Now one may apply the second rule 6x 4 isUse the distributive property to multiply 3x^{4}18x^{3}24x^{2} by x1 and combine like terms Use the distributive property to multiply 3 x 4 − 1 8 x 3 2 4 x 2 by x 1 and combine like terms 3x^{5}15x^{4}6x^{3}24x^{2} 3 x 5 − 1 5 x 4 6 x 3 2 4 x 2 Expand 3x^{5}15x^{4}6x^{3}24x^{2} 3 x 5 − 1 5 x 4 6 x 3 2 4 x 2 View solution steps Solution Steps f ( x ) = 3 x ^ { 2




Which Of The Following Polynomial Functions Is Graphed Below A F X X 5 X 1 2 X 1 B Brainly Com



How Do You Find All The Zeros Of F X X 4 4x 3 4x 2 36x 45 Socratic
0Adding 2 both sides 2 – 3x <So, the inverse of f(x) = 2x3 is written f1 (y) = (y3)/2 (I also used y instead of x to show that we are using a different value) Back to Where We Started The cool thing about the inverse is that it should give us back the original value When the function f turns the apple into a banana, Then the inverse function f1 turns the banana back to the apple Example Using the formulas fromX^2(y(x^2)^(1/3))^2 = 1 Natural Language;



How To Find F 2 If F X 2 5x 4 X 3 Quora



How Do You Find The Discriminant Of X 2 2x 4 0 And Use It To Determine If The Equation Has One Two Real Or Two Imaginary Roots Socratic
F(x 1) = 3(x 1) 4 = 3x 7 Domain and Range The domain of a function is the set of values which you are allowed to put into the function (so all of the values that x can take) The range of the function is the set of all values that the function can take, in other words all of the possible values of y when y = f(x) So if y = x 2, we can choose the domain to be all of the real numbersMinimum f = 463, nearly This is improved to 8sd, \displaystyle {} , using an iterative numerical methodB and f(x) ≥ f(z) for every z in both (a, b) and




Maximum Value Of Function F X Frac X 4 X 2 X 6 2x 3 1 When X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
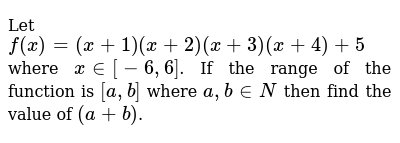



Let F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 5 Where X In 6 6 If The Range Of The Function Is A B Where A B In N Then Find The Value Of A B
Consider x^ {2}4x3 Factor the expression by grouping First, the expression needs to be rewritten as x^ {2}axbx3 To find a and b, set up a system to be solved a=3 b=1 Since ab is positive, a and b have the same sign Since ab is negative, a and b are both negative The only such pair is the system solutionKnowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &Beyond simple math and grouping (like (x2)(x4)), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expect You can also use pi and e as their respective constants Please note You should not use fractional exponents For example, don't type x^(1/3) to compute the cube root of x Instead, use root(x,3
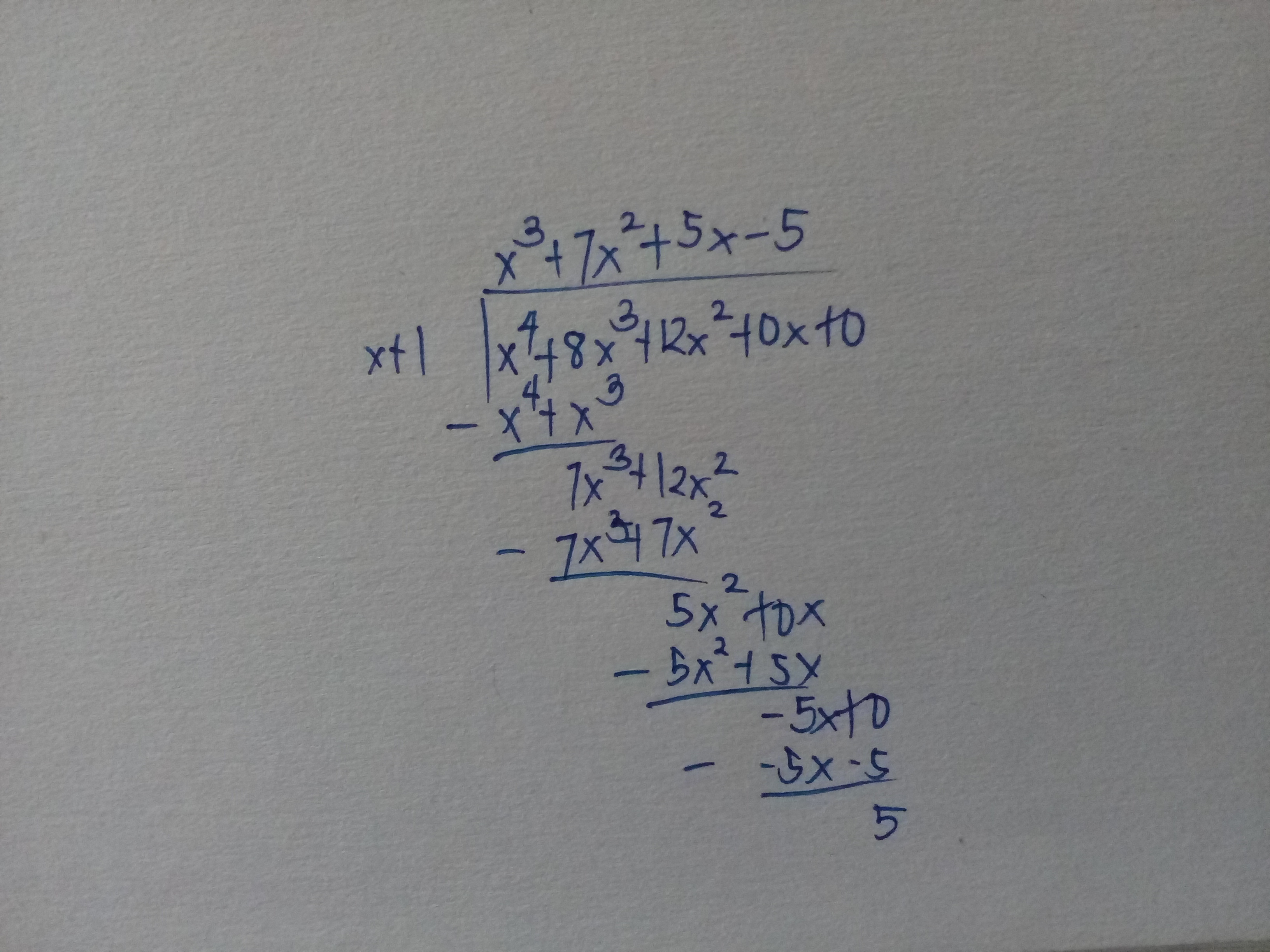



How Do You Find The Remainder When F X X 4 8x 3 12x 2 X 1 Socratic




Binomial Approximation Wikipedia
If x=7 4√3 and xy=1 then 1/x^2 1/y^2=I'm providing Free Online Live Maths Classes &Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!The output f (x) is sometimes given an additional name y by y = f (x) The example that comes to mind is the square root function on your calculator The name of the function is \sqrt {\;\;} and we usually write the function as f (x) = \sqrt {x} On my calculator I input x for example by pressing 2 then 5 Then I invoke the function by pressing
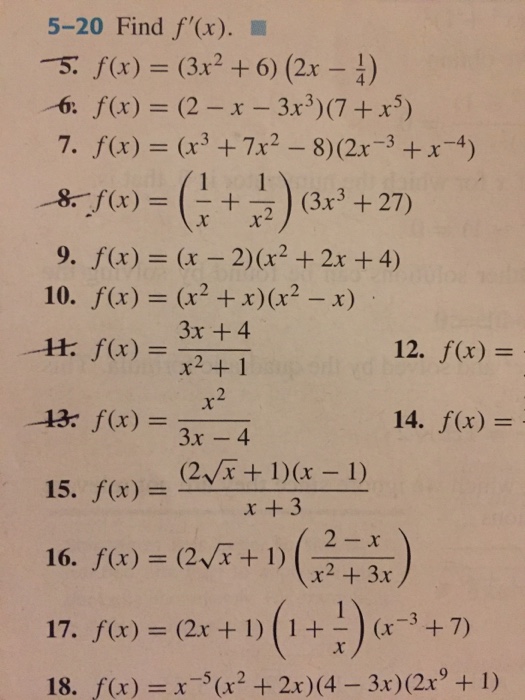



Find F X F X 3x 2 6 2x 1 4 F X 2 Chegg Com




Ex 5 8 4 Verify Mean Value Theorem F X X2 4x 3
Integration by substituting u = axb 2 3 Finding Z f(g(x))g So, substituting u for 3x4, and with dx = 1 3 du in Equation (2) we have Z cos(3x4)dx = Z 1 3 cosudu = 1 3 sinuc We can revert to an expression involving the original variable x by recalling that u = 3x 4, giving Z cos(3x4)dx = 1 3 sin(3x4)c We have completed the integration by substitution It is very easy to generaliseF (x) is decreasing when x = −1 Explanation To determine whether f (x) is increasing or decreasing at x = −1 More Items x^ {2}3x2x64 Apply the distributive property by multiplying each term of x2 by each term of x3 x^ {2}x64 Combine 3x and 2x to get x x^ {2}x2 Add 6 and 4 to get 2




Evaluate 1integral4 X 1 X 2 X 4 Dx Mathematics Shaalaa Com



8 5 Approximations Of Roots Of Functions Newton S Method




Derivative Of F X X 2 1 3 2x 5 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Search Q Solve For X Tbm Isch
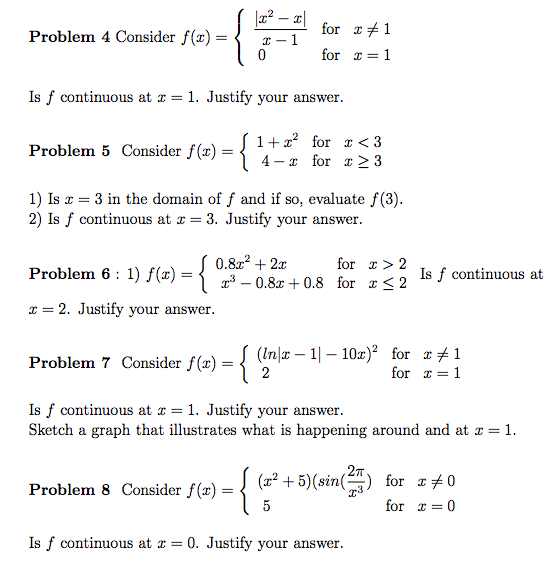



Consider F X X 2 X 0 X 1 For X 1 For X 1 Chegg Com




Let F X X 2 X 3 X 4 And G X F X 1 Then 1 G X Is An Even Function 2 G X Is An Odd Function 3 G X Is Neither Even Nor Odd 4 G X Is



How To Solve X 4 2x 3 3x 2 2x 1 0 Manually Quora
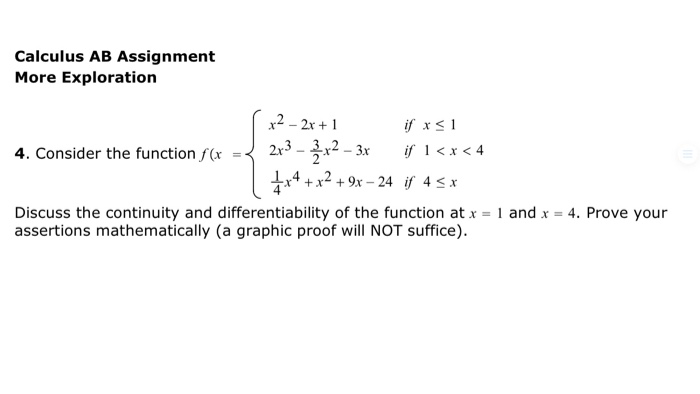



Consider The Function F X X 2 2x 1 If X Chegg Com




How Do You Find F X Using The Limit Definition Given F X X 2 1 2x 3 Socratic




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34




If F X X 1 4 X 2 3 X 3 2 X 4 Then The Value Of F 1 F 2 F 3 F 4 Equals
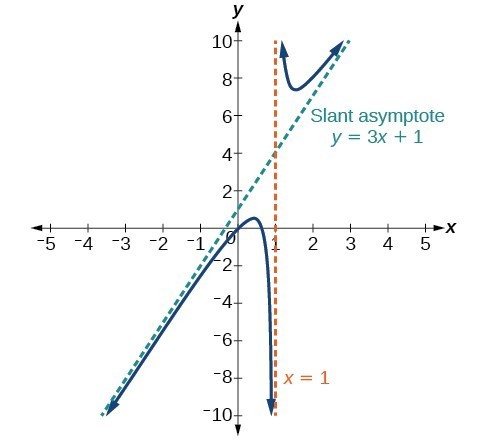



Identify Vertical And Horizontal Asymptotes Math 1314 College Algebra




Exponential Functions Complete Test Ib Mcr3u Youtube
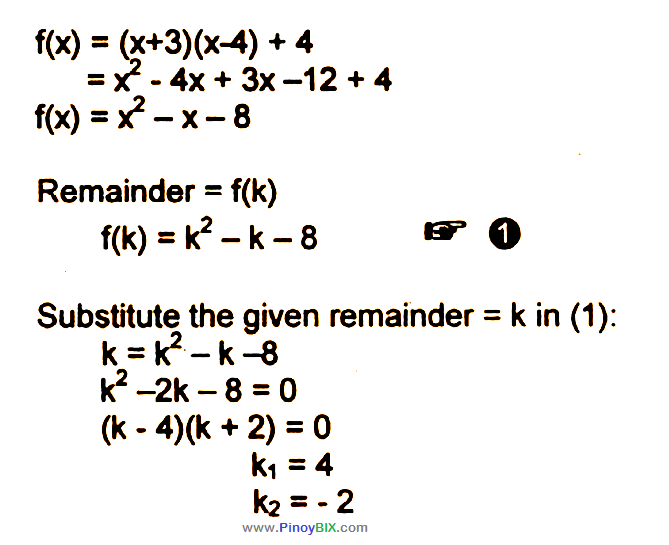



Solution Given F X X 3 X 4 4 When F X Is
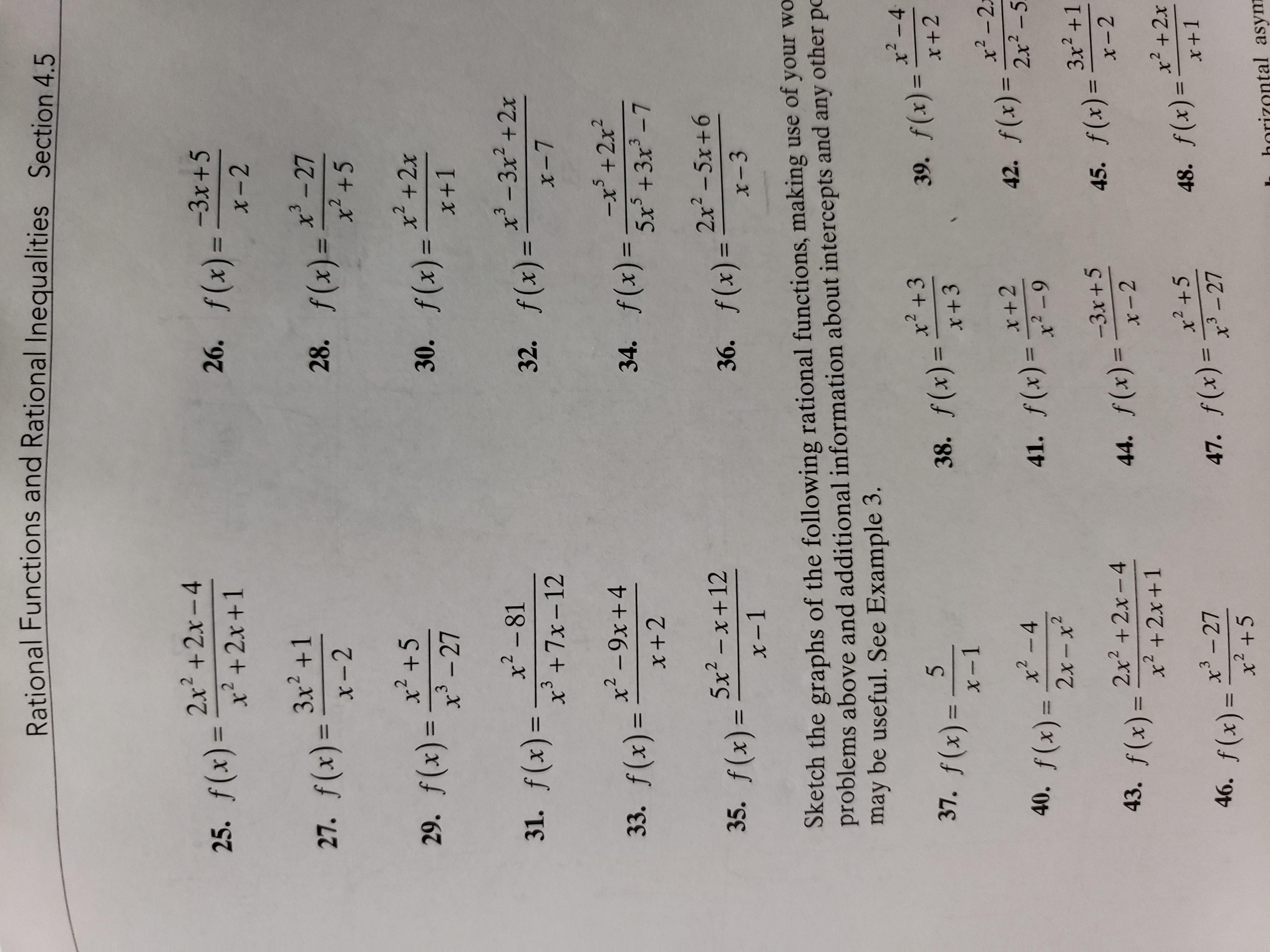



Answered Find Equations For The Vertical Bartleby



Www Lcps Org Cms Lib Va Centricity Domain 3665 Unit 4 day 7 notes a2 Pdf




Warm Up Exercises 1 What Is The Degree Of F X 8x 6 4x 5 3x 2 Solve X 2 2x 3 0 Answer 6 1 I 2 Ppt Download




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X 3 4x 2 3x 1 G X 2 X What Is The Brainly Com




Ex 5 5 16 Find Derivative Of F X 1 X 1 X2 1 X4 1 X8
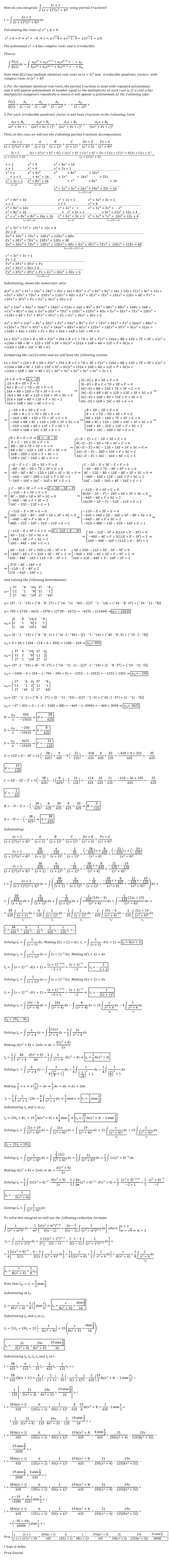



How Do You Integrate Int 2x 1 X 1 3 X 2 4 2 Using Partial Fractions Socratic




Misc 7 Let F X X 1 G X 2x 3 Find F G F G F G



What Is The Inverse Of The Function F X X X 1 Quora




Warm Up Exercises 1 What Is The Degree Of F X 8x 6 4x 5 3x 2 Solve X 2 2x 3 0 Answer 6 1 I 2 Ppt Download




Warm Up Exercises 1 What Is The Degree Of F X 8x 6 4x 5 3x 2 Solve X 2 2x 3 0 Answer 6 1 I 2 Ppt Download




1 Given The Functions F X X 1 And G X 3 X Chegg Com




Quadratic Function Wikipedia




Find The Derivative Of The Function Given By F X 1 X 1 X2 1 X4 1 X8 And Hence Find F 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Let F X X 2 3 4 X 2 3 3 X 4 5 Then D Dx Chegg Com



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




Answered Find Equations For The Vertical Bartleby
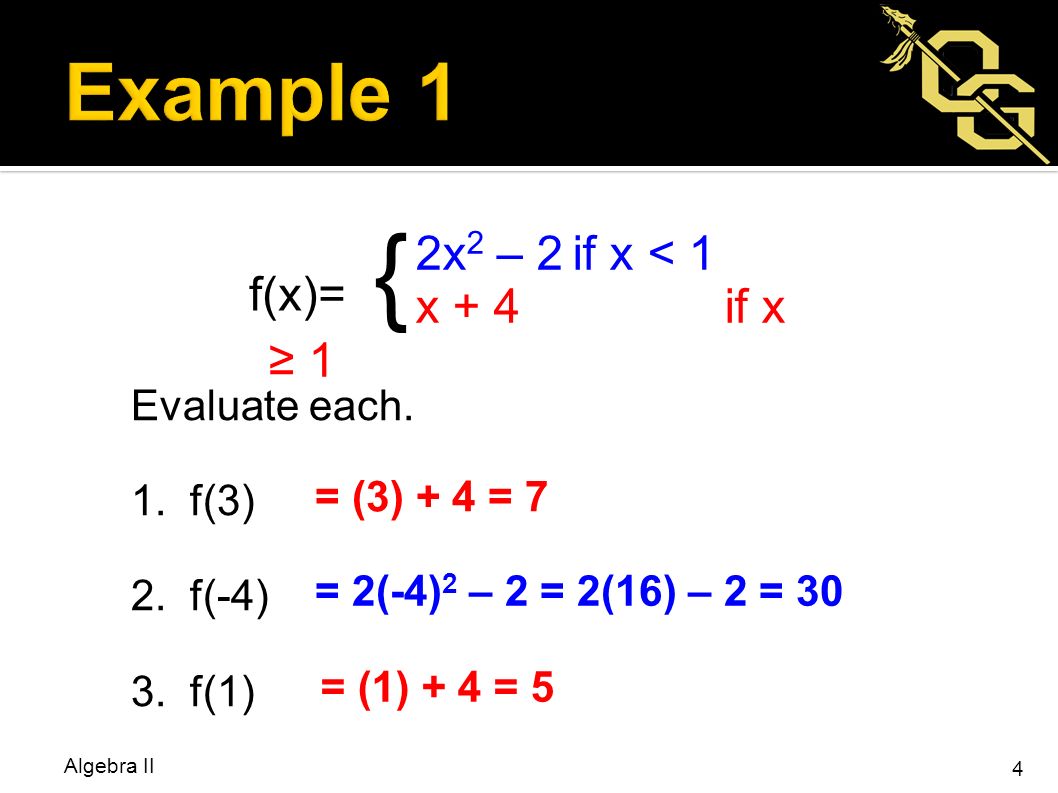



Bellwork Graph Each Line 1 3x Y 6 2 Y 1 2 X 3 Y Ppt Video Online Download




The Domain Of The Function F X Sqrt X 1 X 3 X 2 Is 1 2 Uu 3 Oo B 1 2 Uu 3 Oo C 1 2 Uu 3 Oo D None Of These




The Islamic University Of Gaza Faculty Of Engineering



1




How Do You Integrate F X X 2 1 X 2 1 X 4 Using Partial Fractions Socratic




1 2 Solving Equations By The Quadrus Method Levels 1 2 3 G Day Math
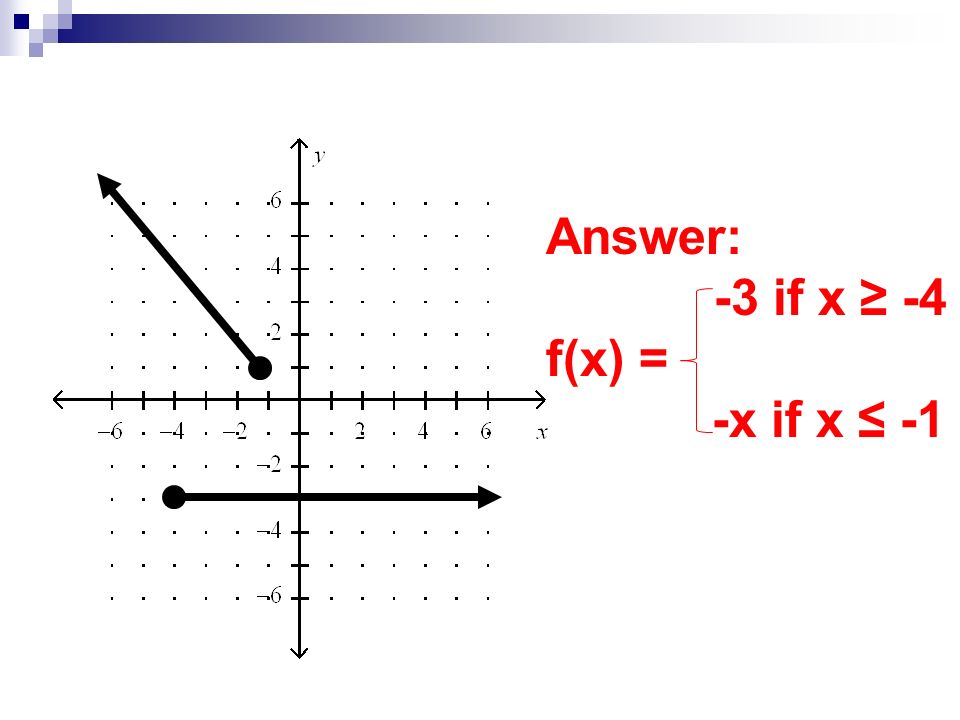



Answer 3 If X 4 F X X If X Ppt Video Online Download
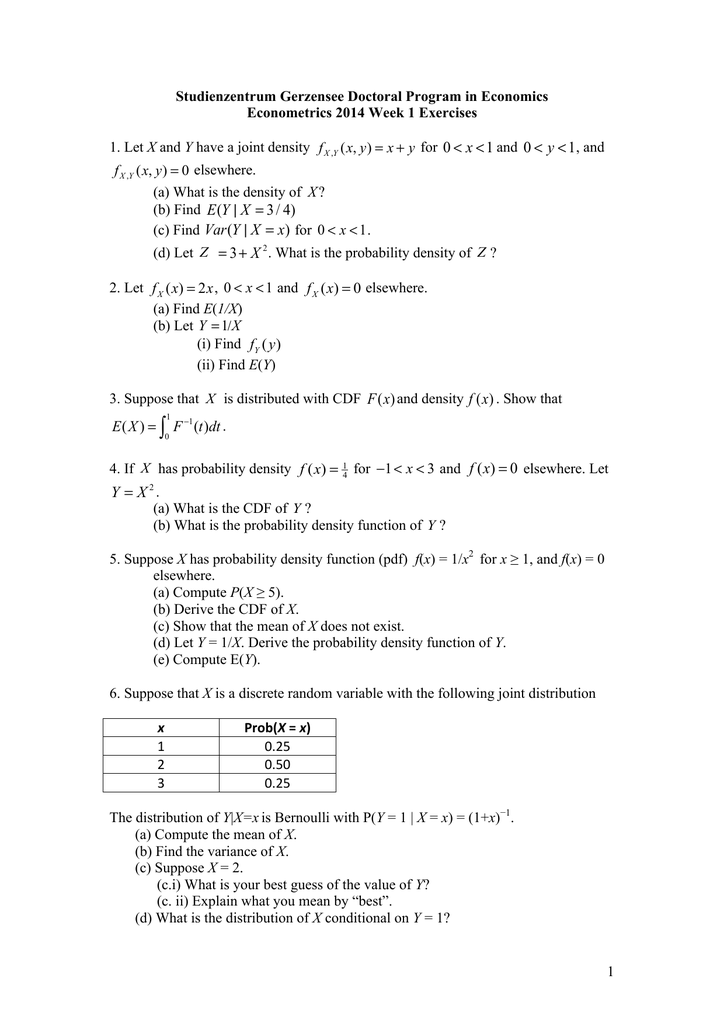



0 1 X




Content Polynomial Function Gallery



What Are The Roots Of The Function F X 2 X 1 X 2 2x 3 With X R Quora
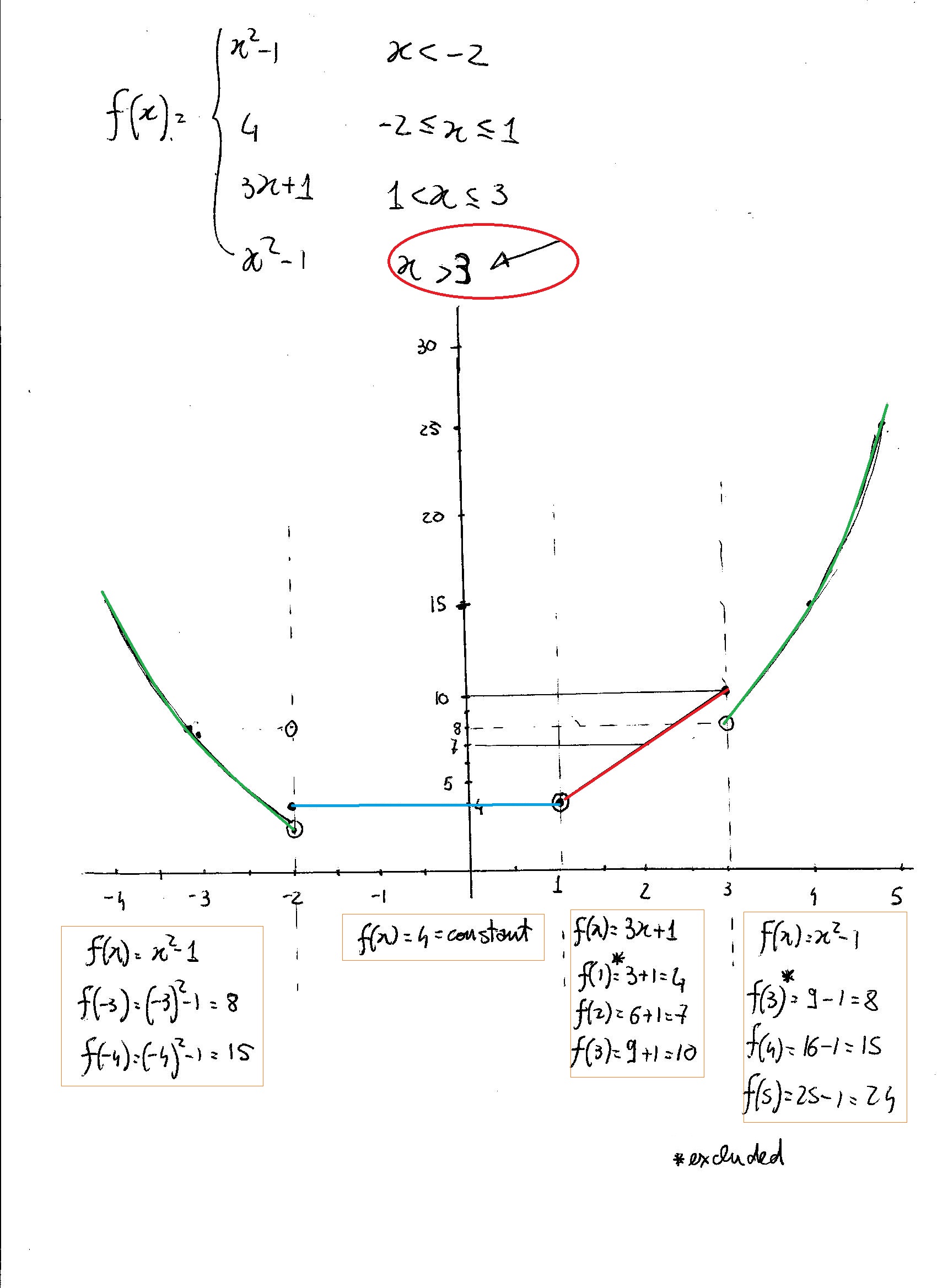



How Would You Graph F X If F X X 2 1 X 2 4 2 X 1 3x 1 1 X 3 X 2 1 X 1 How Would You Evaluate The Function At The Indicated Points F 3 F 2 F 5 F 3 Socratic



What Are The Values Of X Satisfying X 2 X 3 1 Quora



F X X 2




If F 2 X F 1 X1 X X 3 X 1 1 F X 0 Then Find F 2 Where Is The G I F




4 2 Linear Approximations And Differentials Mathematics Libretexts
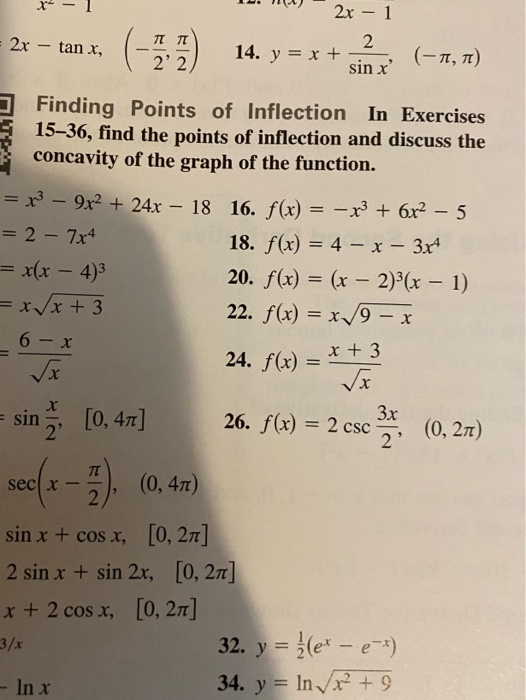



X 1 11 I 2x 1 2x Tan X 14 Y X 2 Chegg Com
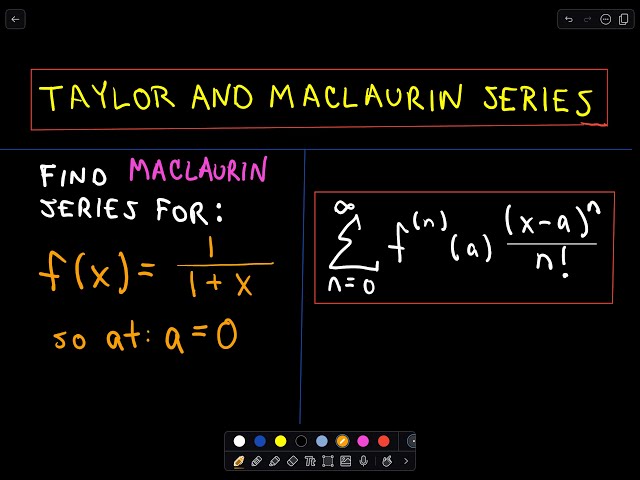



Finding A Maclaurin Series Expansion Another Example 1 Youtube




1 Functions




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy




اسئلة محلولة عن الدوال والنهايات



View Question Just A Few Questions



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




Misc 13 Find Points F X X 2 4 X 1 3 Has Local Maxima




Find Equation Of Tangent To Y X 3 1 X 2 Find Interval Where




Multiplying And Dividing Functions Article Khan Academy



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf
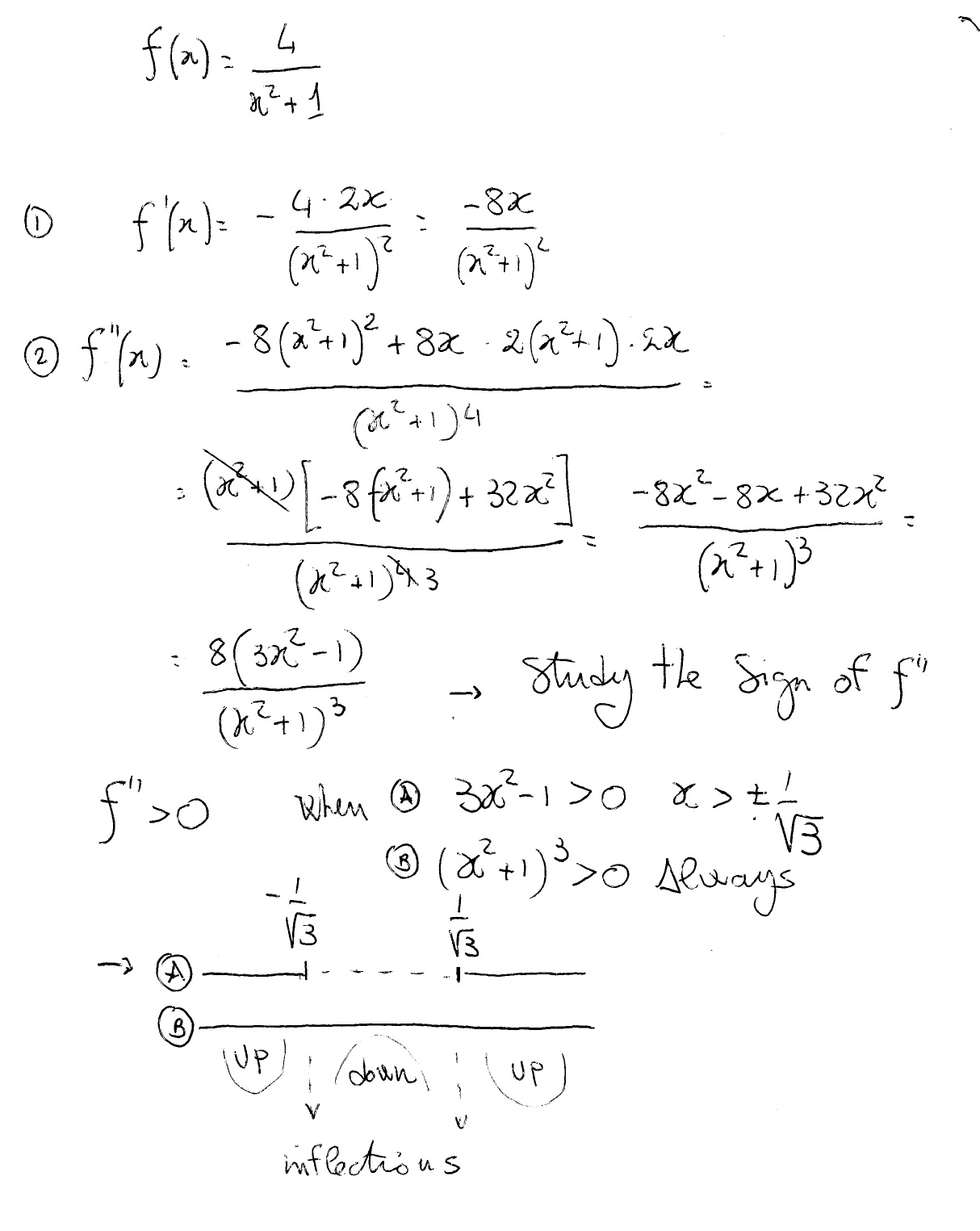



How To Find If A Function F X 4 X 2 1 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down Socratic




1 Let F X X2 1 And G X 3x A Evaluate Chegg Com




Polynomial Functions




Section Find The First Four Derivatives Of F X X 4 2x 3 3x 2 5x Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿